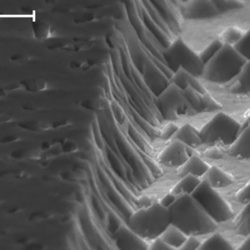
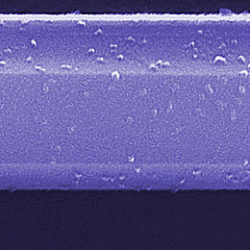
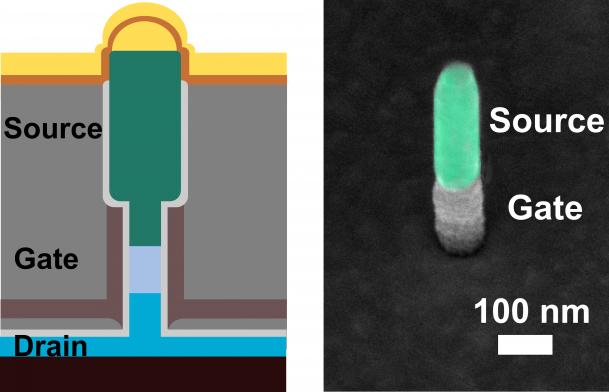
Neuromorphic computers with one step closer due to neurotransistors
Especially activities in the field of artificial intelligence, like teaching robots to walk or precise automatic image recognition, demand ever more powerful, yet at the same time more economical computer chips. While the optimization of conventional microelectronics is slowly reaching its physical limits, nature offers us a blueprint how information can be processed and stored Read more about Neuromorphic computers with one step closer due to neurotransistors[…]