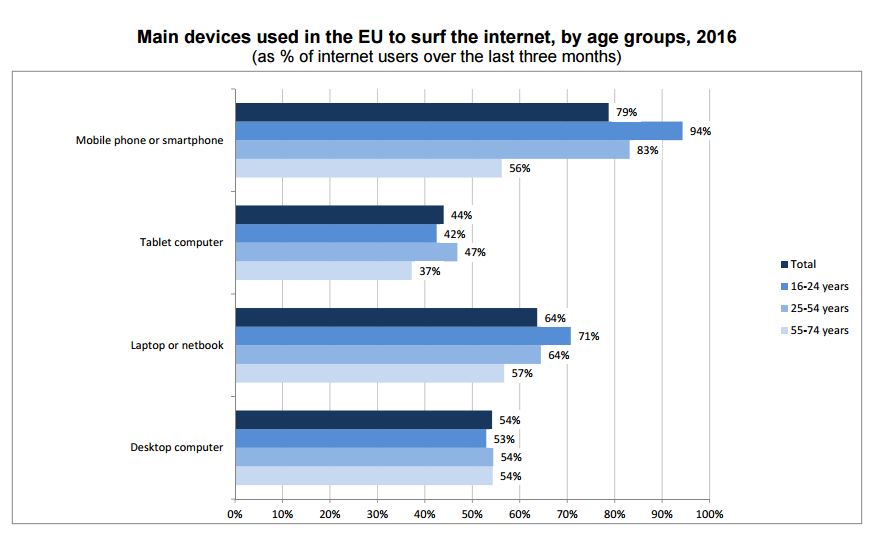
More than 80% of persons aged 16 to 74 in the European Union (EU) used the internet in 2016, in many cases via several different devices. Mobile phones or smart phones were the device most used to surf the internet, by over three-quarters (79%) of internet users. They were followed by laptops or netbooks (64%), desktop computers (54%) and tablet computers (44%).
During the last twelve months, more than 70% of internet users in the EU provided some kind of personal information online, many of them undertaking different actions to control access to this personal information on the internet. Almost half of them (46%) refused to allow the use of personal information for advertising and 40% limited access to their profile or content on social networking sites. In addition, 37% of internet users read privacy policy statements before providing personal information and 31% restricted access to their geographical location. This information, issued by Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union, is part of the results of the survey conducted in 2016 on ICT (Information and Communication Technologies) usage in households and by individuals.
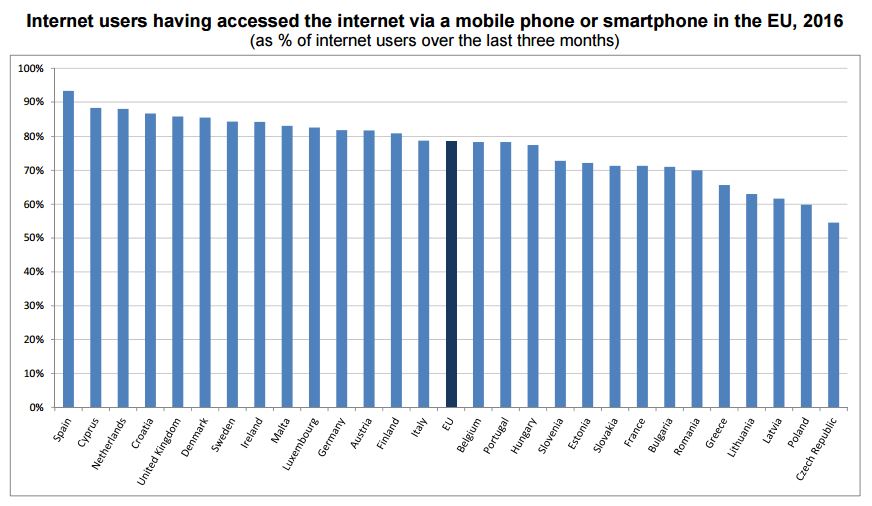
Highest shares of surfers via mobile phone or smartphone in Spain, Cyprus and the Netherlands
Mobile phones or smartphones were the devices the most used in 2016 by internet surfers in every EU Member State, except for the Czech Republic, Estonia, Lithuania, Poland and Slovakia where it was laptops or netbooks. In 2016, the highest proportion of internet users having accessed the internet via a mobile phone or a smartphone was registered in Spain (93% of those having used the internet over the last three months), ahead of Cyprus and the Netherlands (both 88%), Croatia (87%), the United Kingdom (86%) and Denmark (85%). At the opposite end of the scale, the lowest share was recorded in the Czech Republic (55%), followed by Poland (60%), Latvia (62%), Lithuania (63%) and Greece (66%).
Among Member States, laptops or netbooks were used to surf the internet by at least three-quarters of internet users in the Netherlands (80%), Finland and Belgium (both 78%) and Denmark (76%), while desktop computers were used by more than two-thirds of internet users in Hungary, Luxembourg and Romania (all 68%) as well as Germany (67%). Finally, tablet computers were used to access the internet by less than half of internet surfers in a vast majority of Member States, with the exceptions of the Netherlands (66%), the United Kingdom (61%), Denmark (56%), Germany (55%), Luxembourg (53%) and Finland (52%).
At EU level, young individuals aged 16-24 mostly preferred accessing the internet via a mobile or a smart phone (94%) as well as via a laptop or a netbook (71%), while the use of a tablet computer was most popular among those aged 25-54 (47%).
Disparities in ways used to manage access to online personal information
Disparities between the EU Member States can be observed in the way internet users managed access to their personal information on the internet in 2016. In twelve Member States, refusing to allow the use of personal information for advertising came first, with the highest shares being registered in Luxembourg (72% of internet users over the last twelve months) and Finland (71%), followed by the Netherlands (65%), Denmark (60%) and Estonia (59%). In nine Member States, access to personal information on the internet was principally managed through reading privacy policies, while this was managed via limiting access to profile or content on social networks in six others. Although restricting access to geographical location was not the most used tool in any Member States, more than half of internet users did so in Luxembourg (63%), Finland (58%), Austria and the Netherlands (both 52%).

Geographical information
The European Union (EU) includes Belgium, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Croatia, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Hungary, Malta, the Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
Methods and definitions
The data source is the 2016 Community survey on ICT usage in households and by individuals. The survey covered individuals aged 16-74. In most countries it was conducted in the second quarter of 2016. Individuals were asked about frequency of internet use and about activities they had carried out on the internet in the last three or twelve months prior to the survey, at home or at any other location.
For more information
Eurostat website section on digital economy and society statistics.
Source: Eurostat Press Office