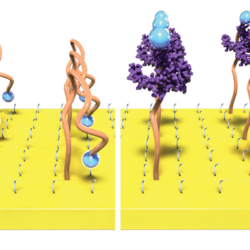
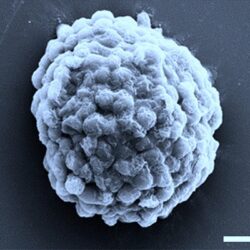
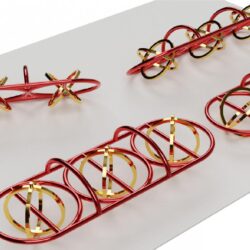
New technology paves way for sensitive bioelectronic diagnostics
The molecules in our bodies are in constant communication. Some of these molecules provide a biochemical fingerprint that could indicate how a wound is healing, whether or not a cancer treatment is working or that a virus has invaded the body. If we could sense these signals in real time with high sensitivity, then we Read more about New technology paves way for sensitive bioelectronic diagnostics[…]